Ako dosahuje súprava centrálneho venózneho katétra lekárske účely prostredníctvom synergie rôznych komponentov?
Analýza základných komponentov súpravy
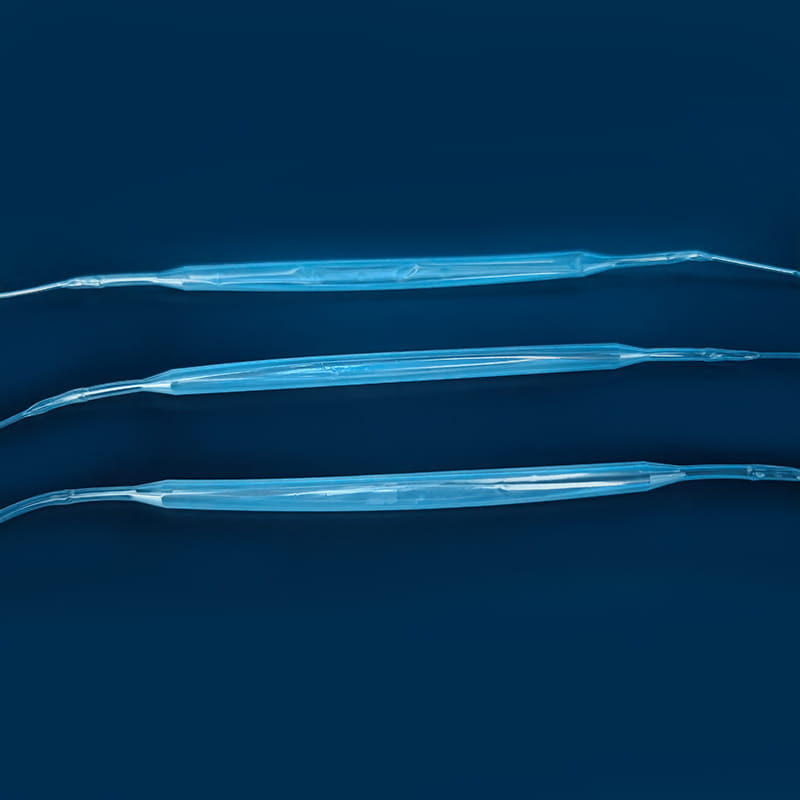
Ten súprava centrálneho venózneho katétra Obsahuje rôzne kľúčové komponenty, z ktorých každá hrá v celom procese lekárskej prevádzky jedinečnú a nenahraditeľnú úlohu. Prvým je centrálny venózny katéter, ktorý je základnou súčasťou súpravy a je kanál spájajúci strednú žilu mimo tela a vo vnútri tela. Jeho materiál je zvyčajne vyrobený z lekárskeho polyuretánu alebo silikónu. Takéto materiály majú dobrú biokompatibilitu a môžu účinne znížiť odmietnutie cudzích orgánov tela a znížiť riziko komplikácií, ako je napríklad infekcia. Rôzne typy centrálnych venóznych katétrov majú svoje vlastné charakteristiky v štruktúre a funkcii. Katétre s jedným lumenom sú vhodné na potreby jednej liečby, zatiaľ čo katétre s dvojitým žiarením alebo viacerým lumenom môžu súčasne vykonávať rôzne lekárske operácie, ako je infúzia, zber krvi a podávanie liečiv, čo výrazne zlepšuje účinnosť a pohodlie lekárskych operácií. Pokiaľ ide o dizajn, niektoré povrchy katétra sú ošetrené špeciálnymi povlakami, aby sa ďalej zvýšili antitrombotické vlastnosti; Niektoré sú tiež označené stupnicami, ktoré uľahčujú zdravotnícky personál, aby presne pochopili hĺbku vloženia.
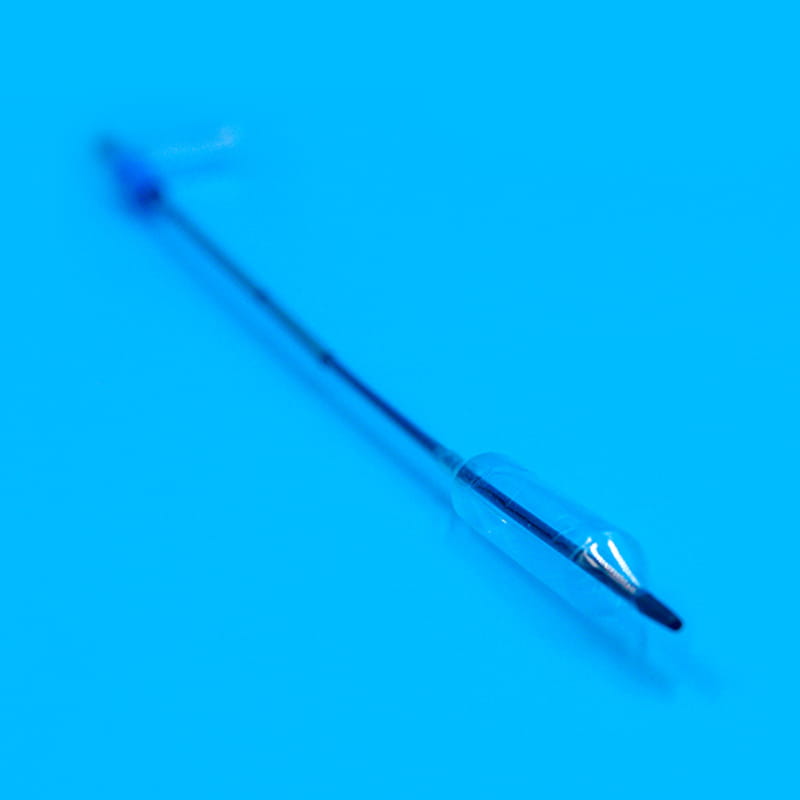
Ten cannula plays a pioneering role in the central venous catheter kit. When performing a central venous catheter insertion operation, the cannula is first used for percutaneous puncture into the vein. Its needle tip adopts a bevel cutting process. This design is sharp and precise, and can quickly and accurately penetrate the skin and vein wall with minimal resistance, opening a channel for the entry of subsequent components. The needle core and outer sleeve of the cannula needle are closely matched. When the cannula needle successfully enters the vein, the inner needle core is removed through a special separation mechanism, and the outer sleeve with a certain hardness and flexibility will remain in the vein as a guide channel for subsequent guide wires and other components to enter. To ensure the accuracy of puncture, some cannula needles are also equipped with ultrasound guidance adapters, which can be used with ultrasound equipment to observe the puncture path and blood vessel status in real time.
Ten guidewire is a key tool for precise positioning and guidance in the central venous catheter kit. After the cannula needle establishes the initial channel, the guidewire will be sent into the vein through the cannula. The outer layer of the guidewire is usually woven from medical-grade stainless steel wire, and the inner layer is a nickel-titanium alloy core. This structure gives the guidewire good flexibility and maneuverability. Doctors can use the J-shaped or straight head design of the guidewire tip to flexibly turn and guide it in the blood vessel through in vitro operation, and accurately send it to the target position. Some high-end guidewires also have a hydrophilic coating, which becomes lubricated after contact with blood, further reducing friction damage to the inner wall of the blood vessel. The existence of the guidewire makes the insertion path of the central venous catheter clearer and more controllable, laying a solid foundation for the smooth insertion of the subsequent catheter.
Ten role of the dilator in the central venous catheter kit should not be ignored. Since the diameter of the vein is relatively thin, and the central venous catheter needs to be smoothly inserted, it is necessary to properly dilate the vein. The dilator usually adopts a conical or cylindrical design, and the material is mostly medical-grade polyethylene. It can enter the vein along the guidewire and expand the channel of the venous puncture site by gradually expanding. During the expansion process, the smooth surface treatment and gradual caliber design of the dilator can reduce damage to the venous tissue while ensuring effective expansion. For special patients, such as those with thin blood vessel walls or sclerosis, there are also special controllable dilators available, and doctors can accurately adjust the expansion strength and range according to actual conditions.
Ten peelable sheath is an important part of the central venous catheter kit to ensure the safe insertion of the catheter. After the dilator completes the dilation of the vein, the peelable sheath will be sent into the vein along the guidewire and dilator. The peelable sheath consists of two symmetrical half sheaths connected by a special locking structure in the middle. When the peelable sheath reaches the appropriate position, the central venous catheter will be inserted into the vein through the sheath. At this time, the medical staff will separate the peelable sheath from the middle lock and remove it from the body through a specific operation technique, while the central venous catheter will be left in the vein. This unique design not only ensures the smooth catheter insertion process, but also avoids unnecessary damage to the vein and catheter. To prevent accidental scratches on the surrounding tissue when the sheath is peeled off, the edge of the sheath is specially rounded and blunted.
Ten fixing device plays a role in stabilizing and fixing the catheter in the central venous catheter kit. In order to ensure that the central venous catheter can maintain a stable position in the patient's body for a long time without displacement or falling off, fixing devices such as sutures, sterile dressings or special catheter fixers will be used to fix the catheter to the patient's skin. The suture fixation method is suitable for patients with long-term catheterization. The catheter is fixed to the skin tissue through delicate suturing operations; the sterile dressing is breathable, waterproof and antibacterial, and can effectively protect the puncture site; the dedicated catheter fixator is made of medical-grade silicone or polymer materials, and can be personalized according to the patient's skin morphology and catheter model through an adjustable buckle design. Appropriate fixation can not only ensure the normal function of the catheter, but also reduce the discomfort and potential risks caused to the patient by the movement of the catheter.
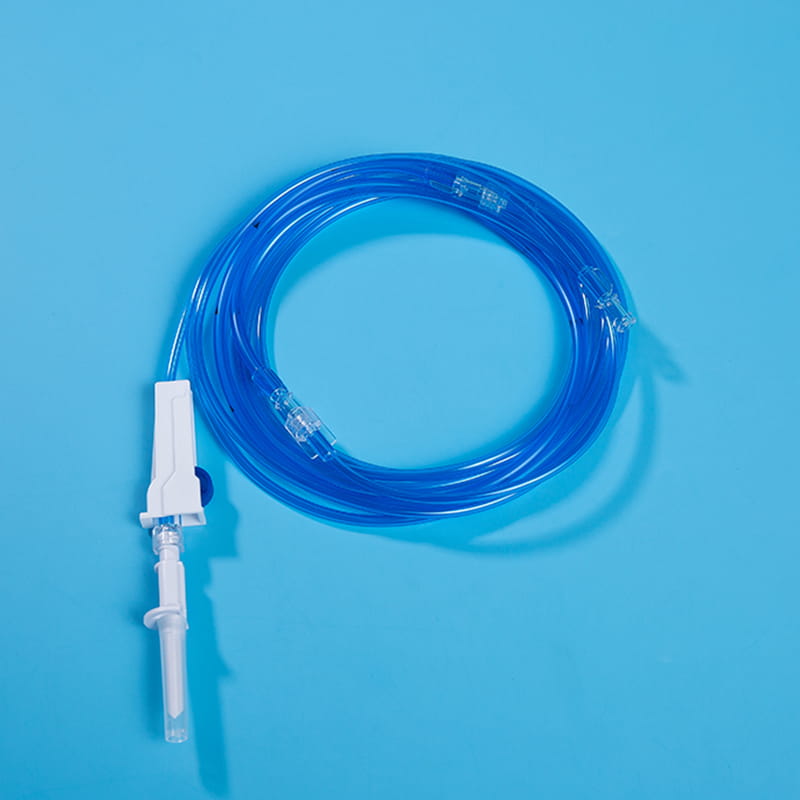
Ten interface for external connection is the bridge between the central venous catheter and external medical equipment. Through these interfaces, the central venous catheter can be connected to infusion sets, syringes and other equipment to achieve various medical operations such as infusion, drug administration, and blood collection. The design of these interfaces has good sealing and compatibility, and common ones include Luer connectors and needleless infusion connectors. The Luer connector is connected by threads to ensure a tight connection without leakage; the needleless infusion connector adopts a diaphragm design, which can complete the infusion operation without acupuncture, reducing the risk of infection. At the same time, some interfaces also have anti-backflow function to prevent blood from reflux and blocking the catheter, and support multiple devices to be connected at the same time to meet complex clinical needs.
Široká škála scenárov klinickej aplikácie
V skutočných lekárskych aplikáciách sú scenáre používania súprav centrálneho venózneho katétra veľmi široké. V oblasti intenzívnej starostlivosti môžu u pacientov s kritickými podmienkami, ktorí potrebujú veľké množstvo infúzie a časté lieky, centrálne venózne katétre poskytnúť rýchly a stabilný infúzny kanál, ktorý uspokojí potreby pacientov pre tekutiny a lieky. Ako príklad, ktorý vezmeme pacientov so septickým šokom, sa počas záchranného procesu musí v krátkom časovom období doplniť veľké množstvo kryštaloidnej tekutiny, koloidnej tekutiny a vazoaktívnych liekov. Centrálny venózny katéter môže zabezpečiť, aby tieto tekutiny a lieky rýchlo vstúpili do krvného obehu a rýchlo opravili stav nárazu. Zároveň je možné vykonávať aj hemodynamické monitorovanie cez centrálny venózny katéter. Doktor spája senzor tlaku s rozhraním katétra, aby získal parametre, ako je centrálny venózny tlak a tlak pľúcnej artérie v reálnom čase, čo lekárom pomáha porozumieť srdcovej funkcii pacienta a stavu krvného obehu v reálnom čase a poskytuje dôležitý základ pre formulovanie presných plánov liečby.
Pri liečbe nádorom veľa chemoterapeutických liekov veľmi dráždi krvné cievy a podávanie periférnymi žilami môže spôsobiť komplikácie, ako je flebitída. Súprava centrálneho venózneho katétra môže umiestniť katéter do centrálnej žily, čo umožňuje chemoterapeutickým liekom priamo vstúpiť do veľkých krvných ciev a rýchlo sa zriediť, čím znižuje podráždenie krvných ciev, znižuje pravdepodobnosť komplikácií a zlepšuje toleranciu a súlad s liečbou pacientov. Napríklad pacienti s rakovinou prsníka, ktorí dostávajú vysoko dráždivé lieky na chemoterapiu, ako je doxorubicín, môžu použiť centrálne venózne katétre na účinné vyhnúť sa závažným dôsledkom, ako je nekróza kože a tkanivový vred spôsobený extravazáciou liečiva. Zároveň u pacientov, ktorí potrebujú dlhodobú a viacnásobnú chemoterapiu, centrálne venózne katétre znižujú bolesť opakovaných vpichov a zlepšujú kontinuitu liečby.
Okrem toho sa v terapii výživy môžu centrálne venózne katétre používať na celkovú podporu parenterálnej výživy pre pacientov, ktorí nemôžu využívať dostatočnú výživu prostredníctvom gastrointestinálneho traktu, ako sú pacienti s dlhodobým kómou a závažné popáleniny. Vďaka vysokej koncentrácii, výživné roztoky s vysokým obsahom kalórií prostredníctvom centrálnej žily môže uspokojiť potreby tela pacienta pre živiny a podporovať uzdravenie pacienta. Berúc pacientom s rozsiahlymi popáleninami ako príklad je ich gastrointestinálna funkcia potlačená v dôsledku traumy a nemôžu normálne stráviť a absorbovať jedlo. V tejto dobe sa roztok all-v-jednom obsahujúci aminokyseliny, emulzie tukov, glukóza a ďalšie zložky podáva cez centrálny venózny katéter, aby sa udržala rovnováha dusíka pacienta, doplňovala energiu požadovanú telom a urýchlila hojenie rán. Zároveň môže zdravotnícky personál monitorovať aj elektrolyty pacienta, hladinu cukru v krvi a ďalšie ukazovatele prostredníctvom centrálneho venózneho katétra a včas upraviť plán výživy.
Prísne a štandardizované prevádzkové postupy
Ten operating procedures of the central venous catheter kit need to strictly follow the specifications and standards. Before the operation, the doctor needs to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, including the patient's age, weight, underlying diseases, coagulation function, etc., and select the appropriate puncture site and central venous catheter type. Common puncture sites include the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein and femoral vein. Different sites have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they need to be carefully selected according to the specific situation of the patient. At the same time, detailed explanations and communication should be given to the patient, and the patient should be informed of the operation process, possible risks and key points of cooperation to obtain the patient's cooperation. During the operation, the principle of aseptic operation must be strictly followed. The puncture site must be disinfected with iodine more than three times, and the diameter of the disinfection range must not be less than 15 cm. A large sterile sheet must be laid to ensure that the entire operation is carried out in a sterile environment. Then follow the steps of trocar puncture, guide wire insertion, dilation with a dilator, insertion of a removable sheath, insertion of a central venous catheter, fixation of the catheter, and connection of an external interface. Taking internal jugular vein puncture as an example, under ultrasound guidance, after determining the puncture point, the trocar is inserted at an angle of 30-45 degrees. After seeing the blood return, it is confirmed that it is in the vein, and then the subsequent components are inserted according to the process. After the operation is completed, the patient needs to be closely observed and cared for, and the patient must be monitored for complications and treated in a timely manner. This includes observing whether the puncture site is red, swollen, or exuded, and changing the dressing regularly; monitoring the patient's body temperature, blood routine, and other indicators to determine whether an infection has occurred; evaluating the function of the catheter to ensure smooth infusion, blood collection, and other operations.
Výzvy a riziká, ktorým čelia
Aj keď súpravy centrálneho venózneho katétra hrajú dôležitú úlohu v oblasti medicíny, počas používania čelia aj niektorým výzvam a rizikom. Infekcia je jednou z najbežnejších komplikácií centrálnych venóznych katétrov. Pretože katéter je v tele po dlhú dobu, je ľahké preniknúť baktérie a iné mikroorganizmy, čo spôsobuje lokálnu infekciu alebo systémovú infekciu. Baktérie vstupujú hlavne do tela kolonizáciou kože v mieste vpichu, kontamináciou konektora katétra a kontamináciou infúzneho systému. Trombóza je tiež problémom, ktorý nemožno ignorovať. Katéter môže stimulovať vaskulárny endotel v krvných cievach, čo spôsobuje zmeny v koagulácii v krvi, čím tvoria trombus. Akonáhle trombus spadne, môže spôsobiť vážne komplikácie, ako je pľúcna embólia. Problémy, ako je blokovanie katétra a vytesnenie katétra, môžu tiež ovplyvniť normálne použitie a účinok liečby centrálneho venózneho katétra. Blokovanie katétra môže byť spôsobené ukladaním drog, krvnou koaguláciou atď.; Presunutie katétra môže súvisieť s faktormi, ako je nesprávna aktivita pacienta a voľná fixácia.
For more information, please call us at +86-18913710126 or email us at .
Cievne intervenčné postupy sú neoddeliteľnou súčasťou modernej kardiovaskulárnej medicíny, najmä ...
Úvod Endobronchiálna trubica s jedným lúmenom sú kritickou zložkou re...
V modernej medicíne sú lekárske katétre nepostrádateľným nástrojom používaným v širokej škále lie...
V zdravotníctve nemožno preceňovať dôležitosť výberu správnych materiálov pre zdravotnícke pomôck...
V ére presnej medicíny nesie malá hadička často bremeno život zachraňujúcich povinností. Ako zákl...
V modernej zdravotnej starostlivosti je presné riadenie tekutín rozhodujúce pre bezpečnosť pacien...